
A variable star, as its name suggests, is a star whose magnitude varies intrinsically, in contrast to eclipsing
binaries whose magnitude varies as a result of one star in the binary system eclipsing the other. True variables are
one of five types, namely Mira stars, semiregular stars, cepheids, eruptive variables and, finally, cataclysmic
variables. Minimum to maximum magnitude can range from days to many months with some variables displaying irregular
periods.
A popular method for the study of variable stars, particularly short-term variables, is by the use of the technique
known as "differential photometry". Rather than measure the (variable) magnitude of a variable star on an absolute
scale, measurements are made over time relative to one or more non-variable star(s) and these differences are then
plotted so as to study and illustrate the relative or differential change in magnitude. Due to the very large number
of variables stars, the field of differential photometry represents one of the key fields in astronomy whereby the
amateur astronomer can make a meaningful and long-lasting contribution to both science and astronomy.
More recently, the search for extrasolar planets (700 discovered so far) has identified yet another interesting
application for the practice of differential photometry whereby the minute drops in magnitude of a star hosting an
exoplanet are studied. Further details for the interested party are available
here.
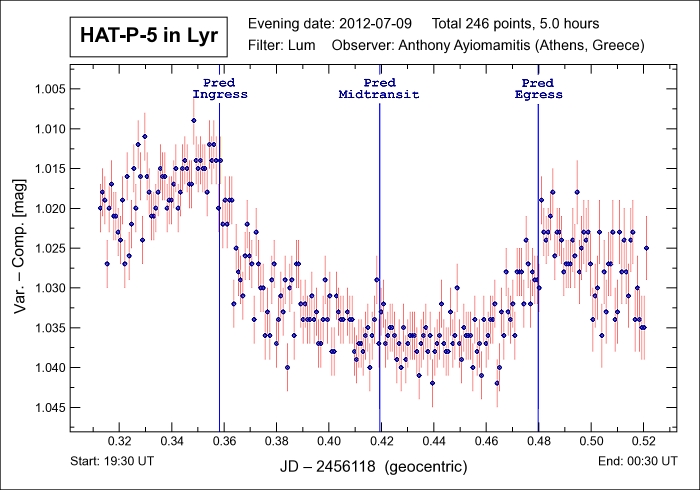
Note: The light curve for exoplanet HAT-P-5b in Lyra depicted below is one of the latest
transitting exoplanets, having being announced late 2007, and represents the fifth discovery by the Hungarian-based
HATNet Project team. HAT-P-5b is characterized with a mass slightly greater that of Jupiter and in spite of a larger
radius (1.257 RJup), thus making this find a slightly low-density hot Jupiter. HAT-P-5b requires 175 minutes
to transit its parent star at a depth of 1.32% with ingress requiring approximately 21 minutes.
The parent star, GSC 2634:1087, is estimated to have a mass of 1.16 solar masses, a radius equivalent to 1.167 solar radii,
a temperature of 5,960° K and to lie at a distance of 1100 light-years with a visual magnitude of 11.95. Further details
regarding HAT-P-5 and HAT-P-5b are available in the paper published by the discovery team led by G. Bakos et al (click
here).
Note: The C- and K-stars used for the purposes of the differential photometry measurements
depicted below were GSC 2634:927 (mag 11.0) and GSC 2634:1063 (mag 11.3) respectively.
|
Parent Star: HAT-P-5 GSC/SAO Catalog: GSC 2634:1087 Constellation: Lyra RA / Dec: 18h 17m 37s / +36° 37' 17" Magnitude: 11.95 Distance: 1100 light-years Exoplanet: HAT-P-5b Period: 2.788491 + 0.000025 d Transit Duration: 175 mins Transit Depth: 13.2 mmag Minimum Mass: 1.06 MJup Radius: 1.257 RJup Pred Transit Details:
|
|
Date: Jul 09-10, 2012 22:30:00 - 03:30:55 UT+3 Location: Athens, Greece Equipment: AP 305/f3.8 Riccardi-Honders AP 1200GTO GEM SBIG ST-10XME SBIG CFW10 SBIG LRGB filters Integrations:
Temperatures:
Software: CCDSoft V5.00.201 AIP4Win V2.4.0 Processing: Reduction Differential Photometry |